We Drive Innovation
Shaping Success Through Elastomers.
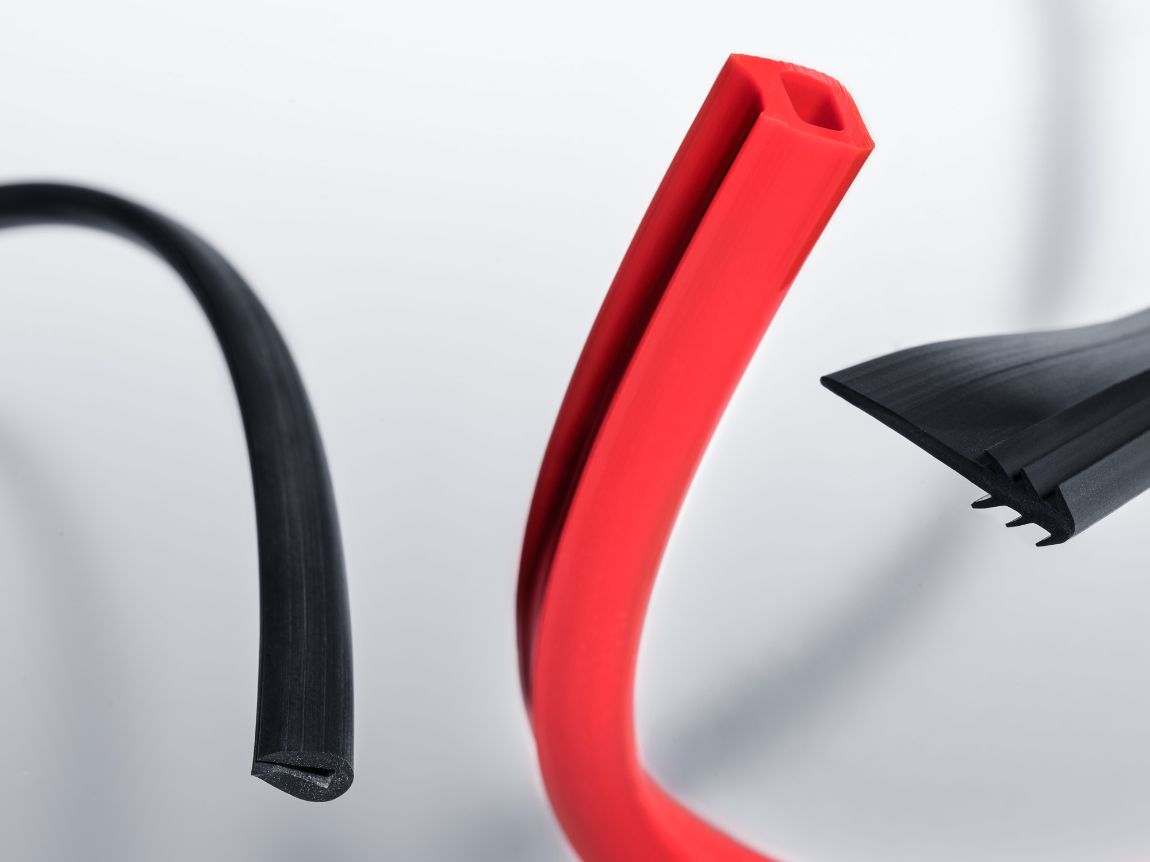
Progressive elastomers are the backbone of tomorrow’s sealing solutions. Our elastomer formulations are meticulously designed to exceed industry standards. We offer a wide range of compounds from standard materials like NBR, HNBR, EPDM, and CR to high-performance compounds such as evolast® FFKM, VMQ, FVMQ, and FKM — all engineered for excellence.
Download our compound table for in-depth information about our performance compounds product range.
Download compound table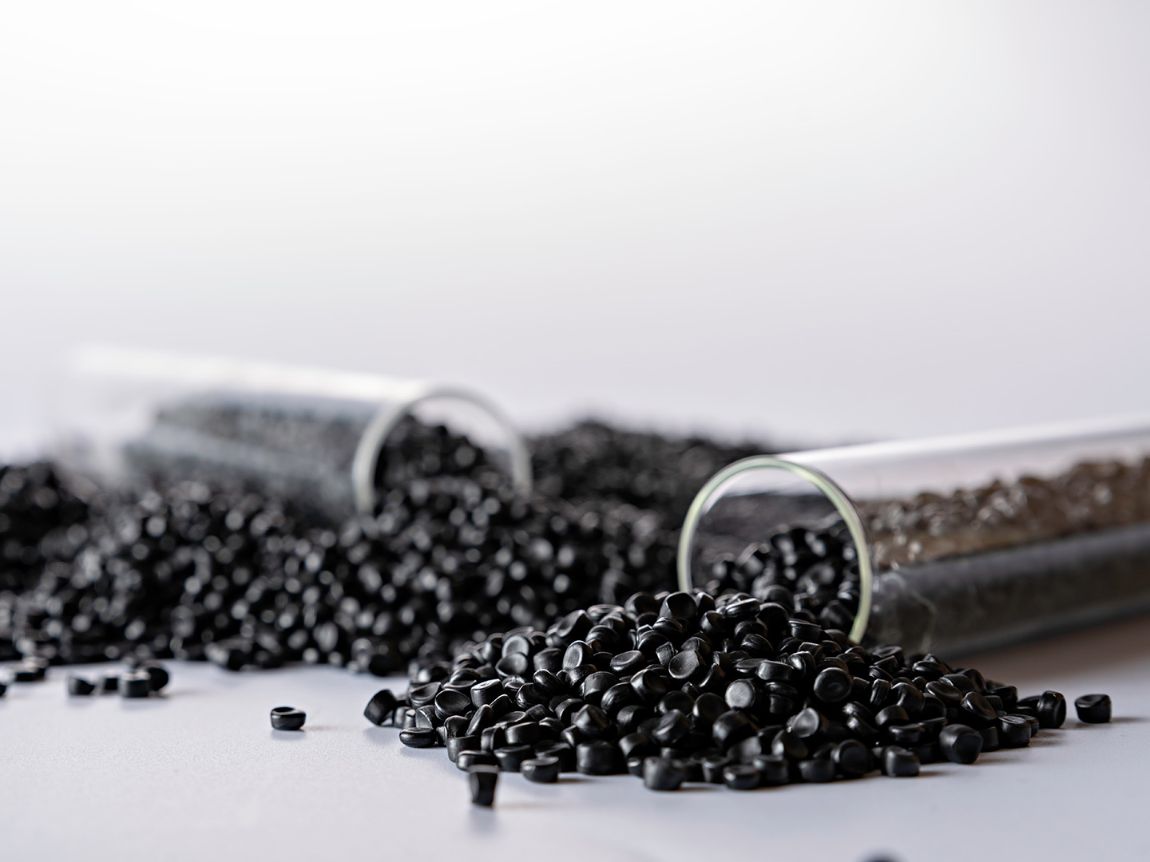
evolast® FFKM: Engineered for Extremes
The Crown Jewel Among Our Elastomeric Compounds.
We engineered evolast® for critical applications in Chemical Processing, Pharma, MedTech, Semiconductors, and Energy. evolast® withstands extreme temperatures up to +340 °C and a wider range of aggressive chemicals than conventional elastomers. It ensures high precision, durability, and consistent performance. Fully developed and produced in-house by the Angst+Pfister Group in Italy, evolast® offers European quality, full traceability, and short lead times.
Learn more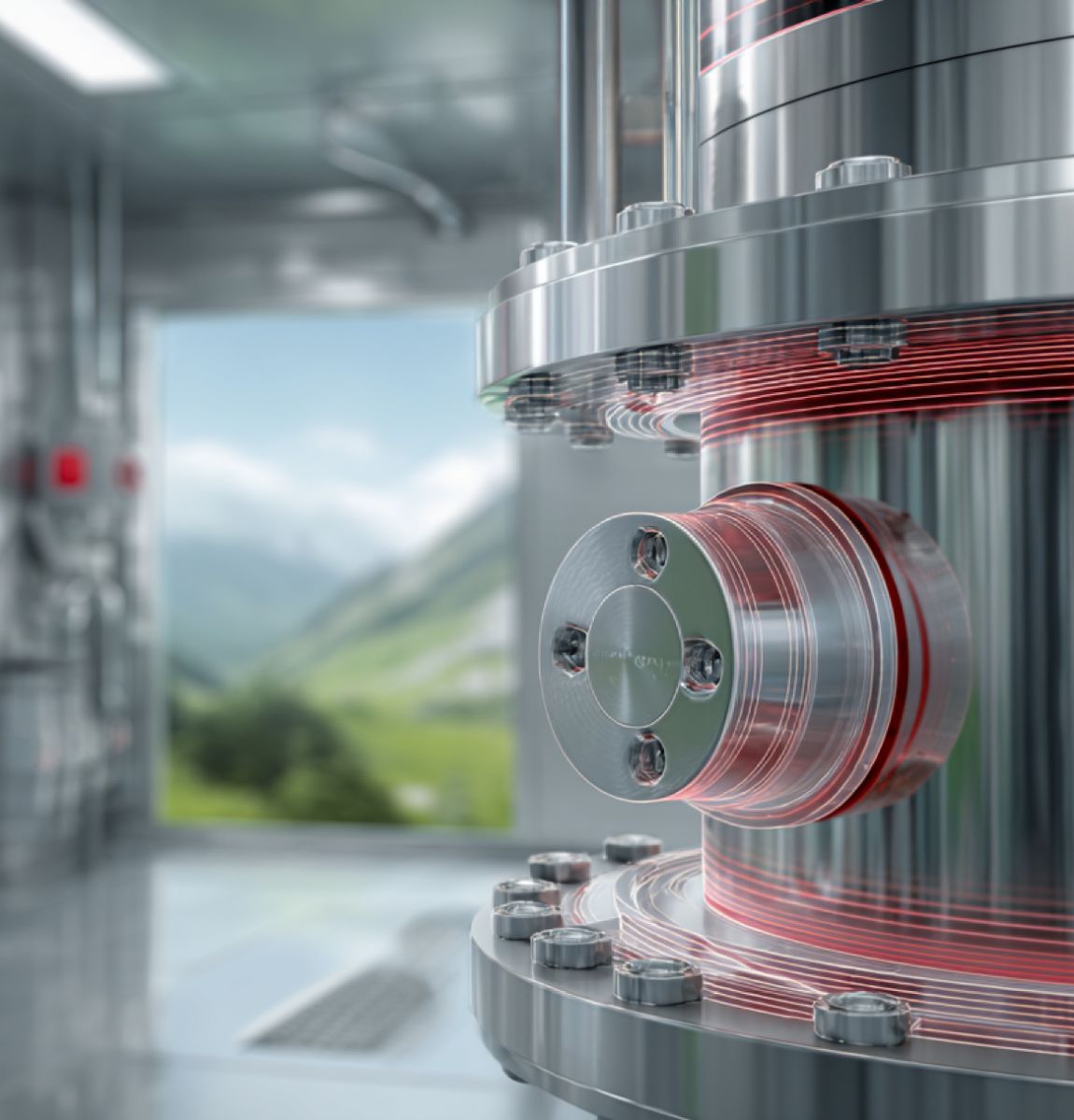
Let’s Talk about your Project!
Request a Free Consultation and Find a Perfect Solution Customized for you.
Based on our assortment, we create and develop an individual solution for your application – or we even develop from scratch a high-performance part for your product to ensure quality & safety. For expert advice and customized solutions tailored to your specific needs, Angst+Pfister service offerings are your go-to resource for Elastomeric Compounds
Let's talk!
